preview
We're still working on this feature, but we'd love for you to try it out!
This feature is currently provided as part of a preview program pursuant to our pre-release policies.
Once you've created a workflow, you can trigger it in three ways: from alerts, manually on demand, or on a schedule.
Choose your trigger method
Select the right approach for your use case:
Trigger from alerts | Trigger from alerts | Run on schedule |
|---|---|---|
Automated incident response | Testing new workflows | Regular health checks |
Auto-remediation (resize EC2, rollback) | Manual operations | Periodic data processing |
Enriched alert notifications | Ad-hoc maintenance | Daily or weekly reports |
API: StartWorkflowRun | API: CreateSchedule |
Sugerencia
When alert conditions are breached, New Relic can automatically trigger workflows by configuring Workflow Automation as a destination. The issueId and accountId are passed automatically. See Send notifications from workflows for setup instructions.
Before you begin
Before triggering workflows, ensure you have:
- Workflow created: A workflow definition already deployed in your account from template or custom-built.
- Account ID: Your New Relic account ID can be found in Account settings.
- Workflow name: The exact name from your workflow definition.
- Required inputs: Values for any parameters your workflow expects.
- Secrets configured: AWS credentials, Slack tokens, or other secrets stored in secrets manager.
Sugerencia
New to workflows? Create your first workflow before trying to trigger it. Start with Use a template for pre-built workflows.
Run workflows on demand
Trigger workflows manually using the StartWorkflowRun API. This executes the workflow immediately with the inputs you provide.
Example: Invoke an AWS Lambda function
The following workflow definition invokes an AWS Lambda function and logs the output. Replace 12345678 with your New Relic account ID.
name: lambda1
workflowInputs: username: type: String defaultValue: "User" key: type: String defaultValue: "${{ :secrets:12345678:USERNAME_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}" access: type: String defaultValue: "${{ :secrets:12345678:USERNAME_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}" token: type: String defaultValue: "${{ :secrets:12345678:USERNAME_AWS_SESSION_TOKEN }}" region: type: String defaultValue: us-east-1
steps: - name: invoke1 type: action action: aws.lambda.invoke version: 1 inputs: awsAccessKeyId: ${{ .workflowInputs.key }} awsSecretAccessKey: ${{ .workflowInputs.access }} awsSessionToken: ${{ .workflowInputs.token }} region: ${{ .workflowInputs.region }} functionName: hello-you payload: user: ${{ .workflowInputs.username }}
- name: logOutput type: action action: newrelic.ingest.sendLogs version: 1 inputs: logs: - message: 'The lambda function message output is:${{ .steps.invoke1.outputs.payload.body }}'To start this workflow, use the following NerdGraph mutation. Before running this mutation, ensure you've stored your AWS credentials using the secretsManagementCreateSecret mutation. For more information, see secrets manager.
mutation { workflowAutomationStartWorkflowRun( # Specify the account where the workflow is defined scope: { type: ACCOUNT id: "12345678" }
# Reference the workflow definition by name definition: { name: "lambda1" }
# Provide input values for the workflow workflowInputs: [ {key: "key" value: "${{ :secrets:testUser123_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}"} {key: "access" value: "${{ :secrets:testUser123_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}"} {key: "token" value: "${{ :secrets:testUser123_AWS_SESSION_TOKEN }}"} {key: "region" value:"us-east-2"} {key: "username" value: "Julien"} ] ) { runId } }Parameters explained:
scope: The account ID where your workflow definition is storeddefinition: The name of the workflow to run (must match thenamefield in your workflow definition)workflowInputs: Key-value pairs that override the default values in theworkflowInputssection of your workflow definition
The mutation returns a runId (for example, 7bd25287-2af8-42e1-b783-80f4e760a40b). Use this ID to query the logs and view the output:
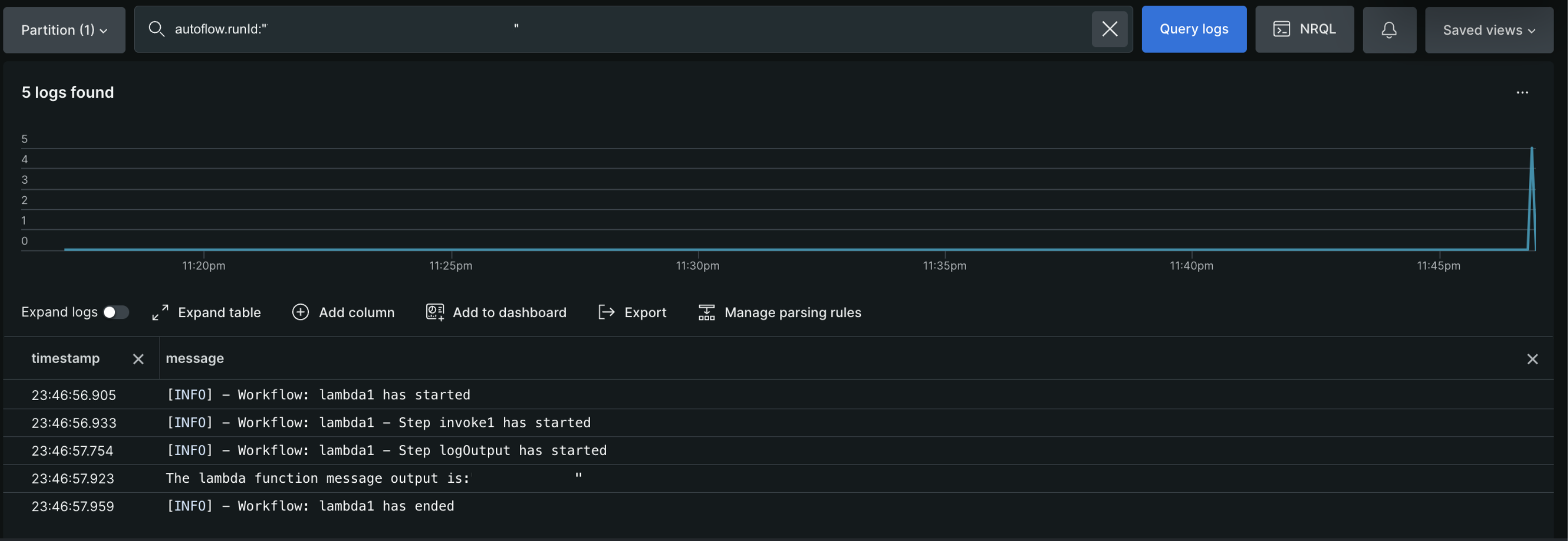
Schedule workflows
Schedule workflows to run automatically at specific times using the CreateSchedule API. Scheduled workflows run recurring tasks without manual intervention.
When to schedule workflows:
- Regular health checks
- Periodic data processing
- Daily/weekly reports
- Scheduled maintenance windows
- Recurring backups or cleanups
Cron expression reference
Schedules use cron expressions to define when workflows run. Format: minute hour day month weekday
Pattern | Description | Example use case |
|---|---|---|
| Every day at 9:00 AM | Daily morning health checks |
| Every weekday at 9:00 AM | Business day operations |
| Every 6 hours | Regular sync operations |
| First day of month at midnight | Monthly reports |
| Every 10 minutes (minimum interval) | Frequent polling, health checks |
| Every Sunday at midnight | Weekly cleanup tasks |
Importante
Minimum schedule interval: Schedules must be at least 10 minutes apart. You cannot schedule workflows to run more frequently than every 10 minutes. For sub-10-minute intervals, consider scheduling every 10 minutes and using a wait step within your workflow. See workflow limits for all scheduling constraints.
Sugerencia
Cron syntax: * means every, / means every nth, - means range. Example: 0 9 * * 1-5 = At minute 0, hour 9, every day, every month, Monday through Friday.
Example: Schedule a daily health check
The following example schedules the lambda1 workflow to run every day at 9 AM Eastern Time:
mutation { workflowAutomationCreateSchedule( # Specify the account where the workflow is defined scope: { type: ACCOUNT id: "12345678" }
# Reference the workflow definition by name definition: { name: "lambda1" }
# Configure the schedule schedule: { # Cron expression: minute hour day month weekday # "0 9 * * *" = every day at 9:00 AM cronExpression: "0 9 * * *"
# Timezone for the schedule timezone: "America/New_York"
# Optional: Schedule name for identification name: "daily-lambda-health-check"
# Optional: Add a description description: "Runs Lambda health check every morning at 9 AM" }
# Provide input values for the workflow workflowInputs: [ {key: "key" value: "${{ :secrets:testUser123_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}"} {key: "access" value: "${{ :secrets:testUser123_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}"} {key: "token" value: "${{ :secrets:testUser123_AWS_SESSION_TOKEN }}"} {key: "region" value:"us-east-2"} {key: "username" value: "HealthCheckBot"} ] ) { scheduleId } }What you get back: scheduleId, Unique identifier for the schedule (use this to update or delete the schedule later)
Workaround: Sub-10-minute intervals
If you need to check something more frequently than every 10 minutes, schedule your workflow at the minimum 10-minute interval and use a wait step within the workflow definition to create additional polling intervals.
Example workflow with 5-minute polling:
name: frequent-health-check
steps: # First check happens immediately when scheduled - name: firstCheck type: action action: newrelic.nrdb.query version: 1 inputs: query: "FROM Transaction SELECT count(*) WHERE appName = 'MyApp' SINCE 5 minutes ago"
# Wait 5 minutes - name: waitStep type: wait seconds: 300
# Second check happens 5 minutes after the workflow started - name: secondCheck type: action action: newrelic.nrdb.query version: 1 inputs: query: "FROM Transaction SELECT count(*) WHERE appName = 'MyApp' SINCE 5 minutes ago"Schedule this workflow to run every 10 minutes using */10 * * * *. This gives you effective 5-minute polling:
- 0:00 - Workflow starts, runs firstCheck
- 0:05 - secondCheck runs (after wait step)
- 0:10 - Next scheduled workflow starts, runs firstCheck
- 0:15 - secondCheck runs (after wait step)
Sugerencia
Workflow duration limit: Remember that workflows have a maximum duration of 7 days. Design your wait steps and polling frequency accordingly. See workflow limits for details.
Manage schedules
After creating a schedule:
- View active schedules: See all scheduled runs in the workflow dashboard
- Update schedule: Use the UpdateSchedule API to change frequency or inputs
- Delete schedule: Use the DeleteSchedule API to stop recurring runs
For complete API documentation, see Workflow Automation APIs.
What's next
- Manage workflows: Edit, duplicate, and monitor execution history.